TIFF vs PNG: What’s The Best Image Format?
Explore the differences between TIFF and PNG, delving into their strengths and weaknesses to determine the optimal image format for your needs.
Image File Formats | Learn | By Ana Mireles
Shotkit may earn a commission on affiliate links. Learn more.
As a photographer, I’m often asked, “Which is better: TIFF or PNG?”
The truth is, it’s not that simple.
Each image format has its strengths and weaknesses.
The best choice depends on what you need from your images.
Over the years, I’ve learned some key differences between these two.
Let’s dive into the world of TIFF vs PNG to discover the best image format for your photography, design and print needs.
TIFF vs PNG: Summary of Differences
- Lossless compression vs. Lossless compression
- Larger file size vs. Smaller file size
- Can’t support transparency vs. Supports transparency
- Slower web loading vs. Faster web loading
- Best for high-quality prints vs. Web graphics/logos
- Less universal support vs. Broad web/software support
- Retains layers vs. Flattened image
What is a TIFF File? (Tagged Image File Format)
- Supports layers
- Best for printing
- Safe
- Lossless and lossy compression options
- Big-size files
- Maximum 4GB
TIFF stands for tagged image file format. This file format is used to save high-quality rasterized images. It can be used with Windows, macOS, and Linux.
The tagged image file format was invented in the mid-1980s for desktop publishing. Adobe holds the copyright to this file format.
Its file extension may be .TIFF or .TIF.
Advantages of TIFF Files
TIFF files are ideal for holding high-quality images or documents containing multiple layers and images. They also have a high level of security that protects them from viruses.
Another advantage is that you can choose to save the files with lossless or lossy compression depending on the file size that you need. You can also save them without compression.
The TIFF format is compatible with most programs. Both Mac and PC have built-in programs that support it – so, you can open it on any computer running Linux, Windows, or Mac OS.
Disadvantages of TIFF Files
Even when you compress an image, TIFF files are often bigger than JPEG files or PNGs. When you include layers, the files can get so big that they reach 1 or 2 GB easily. Yet, the maximum supported size is 4GB.
Another disadvantage is that even if it supports transparency, it’s not compatible with all software.
Where to use TIFF Files
TIFF files are mostly used by printers and anyone in the editorial business because it supports different color modes and up to 32-bit files.
TIFF is also a good solution when scanning documents meant for archival usage. This is especially so for files that hold multiple documents.
What is a PNG File?
- Supports transparency
- High compatibility
- Lossless compression
- Don’t support CMYK
- Big files for online usage
PNG stands for portable network graphics. This was designed in the mid-1990s to overcome some of the shortcomings of the GIF files – for example, the number of colors supported.
Advantages of PNG Files
The most well-known advantage of PNG files is the transparency support. It also offers lossless compression and it’s highly compatible.
Disadvantages of PNG Files
Because PNG files don’t support CMYK, they’re not the best format if you want to print your images.
Where to use PNG Files
PNG files are ideal for vector files with transparencies such as logos. They’re also commonly used for saving documents with lossless compression that doesn’t create such large files as other formats – such as TIFF.
How Much Do You REALLY Know About Photography?! 🤔
Test your photography knowledge with this quick quiz!
See how much you really know about photography...

Comparing TIFF vs PNG Files
Here’s a more in-depth comparison of TIFF and PNG formats.
File Size
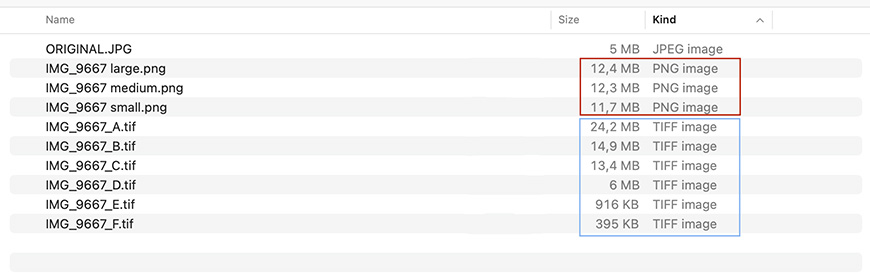
Both file formats offer different saving choices that have a direct impact on the file size. However, TIFF files have more settings which means that you have more control over the final file size.
To give you an example, I opened a 5MB JPEG file in Photoshop and I saved it in the multiple options offered when saving in these image formats without doing any edits on it.
In the end, the TIFF files range from 500 KB to 24,2 MB while the three PNG files are very similar to each other ranging from 11,7 MB to 12,4 MB.
As you can see, the biggest TIFF file is bigger than the biggest PNG file. So, if you want to save with a lossless compression format the PNG format delivers smaller files. Yet, to save more storage space you can use a lossy compression of a TIFF file.
Compression
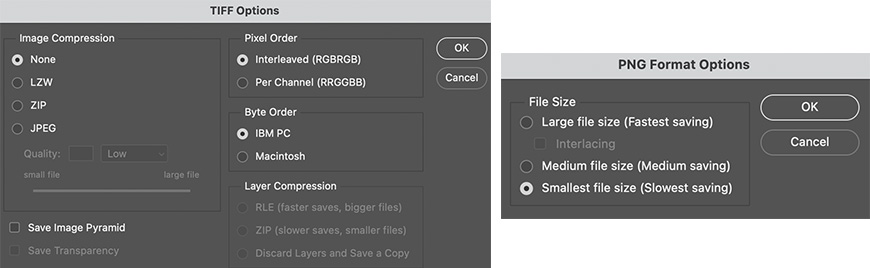
The PNG format only offers lossless compression when you save a file. While you can choose between large, medium, and small file sizes, the result is very similar as they’re all lossless compression options.
On the other hand, the TIFF file format supports both lossy and lossless compression. The lossy compression reduces the file size but it has lower image quality. Instead, a lossless compression TIFF format will have a bigger file size but higher image quality.
Image Quality
The image quality is highly related to the type of compression you use when saving your file. However, if you use a lossless format both PNG and TIFF are high-quality image formats.
However, if you need high-quality images for printing photos, a TIFF file will give you a better-quality print.
Transparency Support
PNG is one of the most popular image formats for saving images with transparency. PNG files also support different degrees of transparency.
Many people don’t know that TIFF files also support transparency. However, not all applications support TIFF transparency. This is why is not the preferred format to work with transparencies.
Color Depth
TIFF files support 16 and even 32 bits per channel while PNG files only support 8 bits per channel. Therefore, a TIFF file has better color depth than PNG and other file formats such as JPEGs.
Expressed in these terms, these don’t seem like such a big difference. However, from 8 bits to 16 bits to 32 bits, you’re not doubling the tonal values – the growth is exponential.
An 8-bit image holds 16.7 million colors while a 16-bit image holds 281 trillion. Hopefully, this gives you an idea of how big a difference it makes to save in PNG or TIFF when you’re thinking about color depth.
If you want to learn more about this topic, I recommend our 8-bit vs 16-bit article.
Compatibility
Both PNG and TIFF files are compatible with most programs. Whether you work with Windows or Mac, you can open both file types with native built-in programs. Therefore, you don’t need to download any specific software.
However, TIFF files support layering. To edit image files that contain layers you do need a photo editing program that supports this feature such as Adobe Photoshop.
As far as web graphics, PNG is also more compatible. The same goes for digital image files that contain transparency.
Metadata Support
The metadata support in PNG files is not as good as in TIFF and other formats. The reading and writing of metadata on a PNG file format are not standardised and therefore it might be a hit-and-miss.
TIFF files however have better metadata support – especially referring to software and not the web.
Layer Support
TIFF is a popular image file because it supports layers. If you’re editing a photograph in Adobe Photoshop using layers and you want to send it to someone who doesn’t use Adobe Creative Cloud, you can save it as a TIFF file.
This way, the other person will be able to access the layers on any software that supports this type of editing. Instead, PNG files don’t support layers. Therefore, you’ll need to flatten your digital images before saving them in a PNG format.
Processing Time
The processing time for TIFF and PNG file formats is very similar. It may change according to the size of the file, though.
Since TIFF files can have multiple images or layers, they can become very heavy files. In this case, a TIFF file is slower.
Another thing that may change the processing time of each file type is compression. For example, when you’re saving a PNG file, you can choose between large, medium, and small.
These file format options have different processing times. A smaller file will take longer because the algorithm is trying to compress the information as much as possible without losing information.
File Flexibility
TIFF files tend to be very flexible. You can use TIFF files to save multiple images in a single file. They’re also very compatible, they support layering, metadata and different types of information such as text, graphics, and raster formats.
PNG files, on the other hand, are great to upload to the web. You can use them to save complex images and web graphics. They’re also smaller in size and more compatible with web pages.
Future Editability
PNG files support lossless compression, the same as TIFF files. When saved this way, both file types can be opened, edited and saved as many times as you like without losing data or image quality. This means that they both have good editable qualities.
However, TIFF files support layering. So, if your editing process requires layers you should use this file type. If you were to save as a PNG, you would need to flatten the document and lose the capability of editing the layers independently.
On the other hand, PNG is a patent-free file format. Instead, the TIFF format belongs to Adobe. Generally speaking, open formats have better chances of maintaining wide compatibility in the future as they’re not subjected to a license.
Usage Purpose
As you can see TIFF and PNG file formats have very distinct characteristics, which makes each of them more suitable for different uses.
Portable network graphics (PNG) are designed for transferring images online. So, their size, compatibility, and characteristics are suited to use on the web.
Instead, tagged image file format files (TIFF) are meant for storing data. It holds more information and therefore it has bigger file sizes. They’re also meant for professional quality printing graphics as it supports CMYK as well as RGB.
What Should You Use? TIFF or PNG?

There isn’t a better file format when it comes to PNG vs TIFF, they simply have different qualities and therefore, different applications.
As I mentioned before, PNG stands for portable network graphics. This file type was designed thinking about online usage. This means that it’s more compatible with web browsers.
So, you should consider PNG files if you need to upload or send a high-quality digital image project.
However, if your project is not for digital usage, then you should consider a TIFF file. This is the most common file format used for professional-quality print graphics because of the color depth.
Also, it supports a CMYK color mode – which a PNG file doesn’t.
If you’re working on a project that holds different documents or multiple layers, then you’ll also need a TIFF file.
Instead, if you’re working on graphics which don’t require big color depth and they use transparency – for example, a logo, then you’re better off with a PNG.
So, if you’re wondering which is the right file format PNG or TIFF, there are many things to consider. However, if you’re looking for a cheat sheet with short answers, here’s something that can help.
- Are you going to print your file? Use TIFF.
- Is your file going to be used digitally? Use PNG.
- Does your file have transparencies? Use PNG.
- Are you working with raster images such as photographs? Use TIFF.
- Are you working with vector graphics? Use PNG.
- Does your file have layers? Use TIFF.
- Do you need to compress images as much as possible even with loss of data? Use a TIFF with lossy compression.
What are other image file formats worth considering?
Aside from PNG and TIFF, there are other popular formats you can consider for your projects.
Digital cameras usually give you the choice between JPEG images or raw files. The JPEG format is the most compatible and it can compress images greatly – this is why it’s become the preferred choice for online usage.
Instead, raw files are ideal for post-processing images as they hold the most amount of information. Raw files have different names depending on the camera manufacturer that creates them. For example, CRW belongs to Canon and NEF to Nikon.
There’s also an open-source format called DNG which is a highly compatible, license-free raw file type developed by Adobe.
GIF file format stands for graphics interchange format and it’s become widely popular because it supports animation.
You can use an online image converter to change the file format of your images if you don’t have editing software that supports the type that you have.
For example, if your program can’t open a raw file from your camera, you can convert it to a DNG file.

Check out these 8 essential tools to help you succeed as a professional photographer.
Includes limited-time discounts.